You may already have come across the term SEER as you start your search for a new HVAC system. Why does this abbreviation matter to me and what is its meaning about different air conditioning systems? In simplistic terms, SEER is short for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio which is a fundamental factor that determines how efficient cooling units are. The higher the number of SEER ratings, the better the performance of efficiency in such units. Our article is going to give you all you need to know about SEER including what it means; how it is computed; and why you should care about it when selecting HVAC systems.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding SEER: What It Means for Your HVAC
Energy Efficiency Ratings
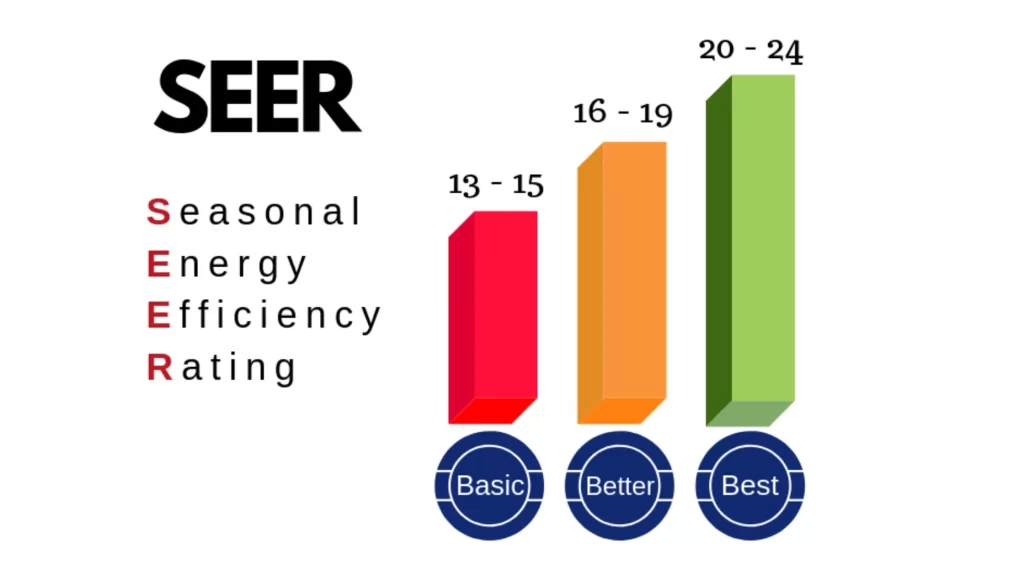
The seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) is an industry-standard used to measure an HVAC unit’s energy efficiency. The higher the rating, the more efficient the unit will be in operation. SEER ratings range from 13 up to 23; where higher values indicate better efficiency and improved energy savings. For residential HVAC systems, a minimum of SEER 14 must be maintained on all devices and appliances but those with higher ratings within this category can lower one’s utility cost.
Lower Energy Usage and Costs
The advantage of a high SEER rating is that a lesser amount of electricity will be spent by the HVAC system for every cooling done by it. Eventually, this results in lower lifetime energy usage as well as reduced utility bills over time. For example, moving from a unit rated at SEER 13 to one rated at SEER 15 has been shown to reduce annual cooling costs by as much as 30%. The initial investment in a more efficient unit will pay off over time through energy savings.
Environmental Benefits
For the environment, it is also better to choose an HVAC unit with a high SEER rating. More power generation greenhouse gas emissions are reduced by more efficient units that use less energy. They will also reduce pollution resulting from burning fossil fuels for electricity. One of the best ways through which homeowners can reduce their carbon footprint and promote environmental sustainability is through upgrading their HVAC systems into new ones.
Longer Unit Life
Normally, the higher the SEER rating, the better quality and stronger the HVAC unit is. Efficient units usually live longer because they do not wear out easily during their life span of operation. A low-rated unit might need replacing after 10-15 while a SEER 15+ unit can work efficiently for 15-25 years. Furthermore, extended longevity of high-efficiency units
How SEER Measures Efficiency in Air Conditioners
The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio or SEER rating is the industry standard for measuring an air conditioner’s efficiency and performance. The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the unit is. SEER ratings range from 13 to 23 for residential air conditioners.
SEER Calculations
- The SEER rating is obtained by dividing the total cooling output of an air conditioner over an entire cooling season by the total electric energy input over the same period. It serves as a way to estimate how much energy needs to be put in to realize a certain level of cooling output. Higher SEER ratings mean lower energy consumption and hence fewer utility bills paid.
Benefits of a High SEER
- Choosing an air conditioner with a high SEER rating provides substantial benefits. A SEER 16-rated unit will use about 30% less energy than a SEER 10 unit, while a SEER 20 unit can use up to 50% less energy. Significant cost savings can be achieved from lower energy usage and reduced utility bills. High SEER units also tend to have better warranties and longer lifespans due to higher-quality components.
Additional Considerations
- While SEER is the most important factor, it is not the only consideration when choosing an air conditioner. You should also consider the size, type, brand, availability of rebates, and overall cost. An oversized or undersized unit will not perform efficiently even if it has a high SEER. Installation and maintenance costs are also significant factors in the overall cost of ownership.
Dive into 'The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners,' your ultimate guide to mastering HVAC systems. From installation to troubleshooting, this updated manual covers it all for both residential and commercial use. Ideal for beginners and experienced technicians seeking comprehensive expertise.
Factors That Influence an AC Unit’s SEER Rating
SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) rating on your AC is based on several important factors. A higher SEER rating means that the unit operates at higher levels of efficiency than one with a lower rating. As a consumer, understanding how these factors impact the SEER can help you make an informed purchase decision when replacing your AC.
Unit Size
- Your AC unit’s SEER rating is significantly influenced by its size or tonnage. Higher SEER ratings are typical for smaller units because larger ones need more energy to operate. For optimal efficiency, select an AC unit whose capacity is a reasonable match for the size of your cooling space. Over-sizing an air conditioning system will greatly reduce efficiency and waste energy.
Compressor Type
- The compressor is what pumps refrigerant through the system in an AC unit. The efficient units are those with scroll compressors as compared to those with reciprocating compressors. Scroll compressors have fewer movable parts; hence, they use less energy. Most efficient of all is the invertor–driven compressors since they can adjust their speed to almost match the cooling needs of any space thereby reducing energy consumption.
Coil and Heat Exchangers
- The condenser coil, evaporator coil, and heat exchanger are responsible for facilitating heat transfer between refrigerant and air in an air conditioner unit. Units with larger coil or heat exchanger surfaces have better heat transfer ability than small ones. Furthermore, copper coils are often used because they have higher thermal conductivity compared to aluminum coils; thus increasing heat transfer rates in cooling coils made from copper rather than aluminum material increases their efficiency too. Heat transfer is also improved by having more fins per inch on the coils and exchangers.
Additional Features
- Additionally, AC units benefit from other features such as programmable thermostats, multiple fan speeds, and airflow controls. A programmable thermostat saves energy by adjusting temperature during these times of no occupancy. The minimum level of operation is controlled through variable fan speeds and airflow control thereby minimizing wastage. This should be considered when comparing different kinds of AC units.
What Does SEER Mean in HVAC
In conclusion, knowing SEER ratings for HVAC systems helps a lot when it comes to buying new units. The higher the SEER, the more energy-efficient the system is. Although these units may cost more upfront, they become cheaper in the end through reduced energy costs. Put into consideration both the size of the unit and its SEER rating while purchasing it for your house. Installation also plays a key role here- a poorly installed unit will not bring about the desired efficiency. With this information, you can choose an appropriate HVAC system that keeps your home comfortable while optimizing energy savings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Exactly Does SEER Stand for in HVAC?
SEER stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio. It’s a metric used to measure the energy efficiency of HVAC systems, particularly air conditioners.
How Does SEER Impact My HVAC System’s Performance?
SEER directly affects your HVAC system’s efficiency. Higher SEER ratings indicate better energy efficiency, resulting in lower utility bills and reduced environmental impact.
What SEER Rating Should I Look for When Purchasing an HVAC System?
For residential HVAC systems, it’s recommended to choose units with a minimum SEER rating of 14. However, higher SEER ratings, such as 16 or above, can provide even greater energy savings.
What Are the Benefits of Investing in a High SEER-Rated HVAC Unit?
Investing in a high SEER-rated HVAC unit offers several benefits, including lower energy consumption, reduced utility bills, extended lifespan of the unit, and decreased environmental impact.
Are There Other Factors Besides SEER That I Should Consider When Buying an HVAC System?
While SEER is an important factor, other considerations such as unit size, compressor type, coil and heat exchanger quality, additional features like programmable thermostats, and proper installation are also crucial for maximizing efficiency and performance.