Electricity powers our modern world, but navigating the world of an electrician can feel like deciphering a foreign language. Whether you’re a seasoned DIY’er or just curious about how things work, getting to grips with common electrical terms is essential for safety and understanding. Let’s break down the most common terms to make them more accessible!
Table of Contents
Toggle
Voltage
Voltage is the force pushing electricity through a wire. Known as potential difference, it’s the difference in the amount of energy that charge carriers have between two points in a circuit – expressed in Volts (V). It’s the “pressure” that drives electrical current. Think of it as the energy behind the flow of electricity.
Current
Current refers to the flow of electricity through a conductor, like a wire. It’s measured in Amps (A), and represents the rate of flow of the electrical charge.
Resistance
Resistance is opposition to the flow of electrical current. Materials with high electrical resistance (like rubber or plastic) restrict the flow, while materials with low resistance (like copper wire) allow current to flow more easily.
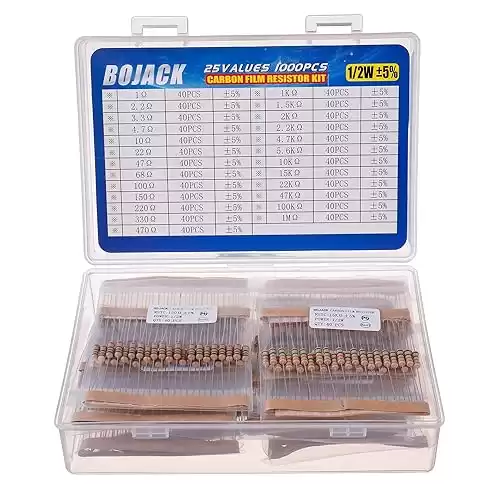
For hands-on learning and practical applications, consider the BOJACK 1000 Pcs 25 Values Resistor Kit 1 Ohm-1M Ohm with 5% 1/4W Carbon Film Resistors Assortment. This kit provides a variety of resistors ideal for experimenting with and understanding resistance in electrical circuits.
Circuit
A circuit is a closed loop through which electricity can flow. It typically includes a power source (like a battery), wires to carry the current, and components (like light bulbs or switches) that use the electricity.
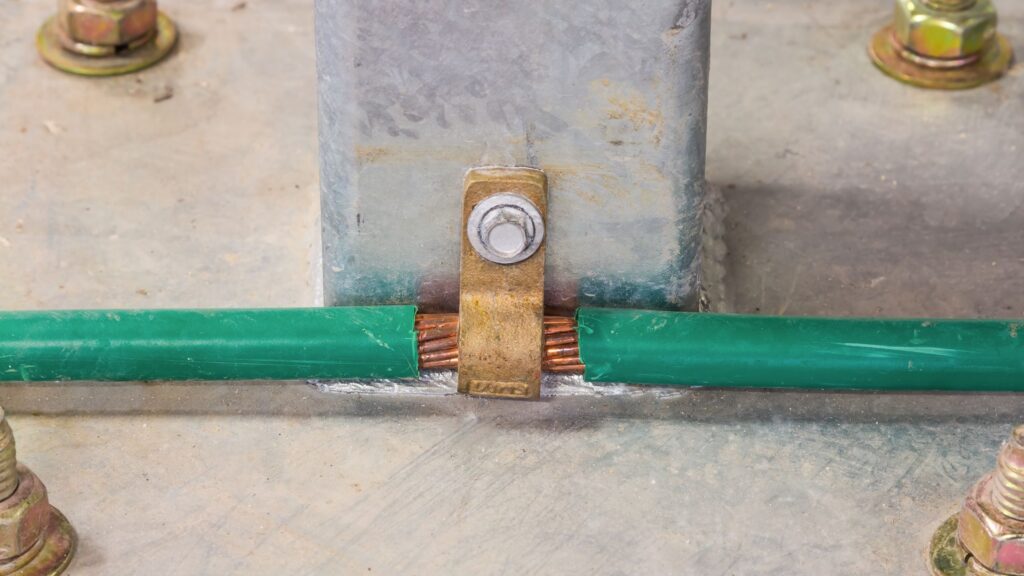
Conductor
A conductor is a material that easily allows electricity to flow through it. Metals like copper and aluminum are commonly used as conductors because they have very low resistance, easily allowing energy to flow.
Insulator
An insulator is a material that prevents or restricts the flow of electricity. Rubber, plastic, and glass (materials with high resistance) are examples of insulating materials used to cover wires and prevent electrical shocks.
Ground
Grounding provides a safe path for electricity to flow into the ground in the event of a fault. Grounding is incredibly important to prevent electrical shock and fire hazards. It’s like a safety valve for excess electricity.
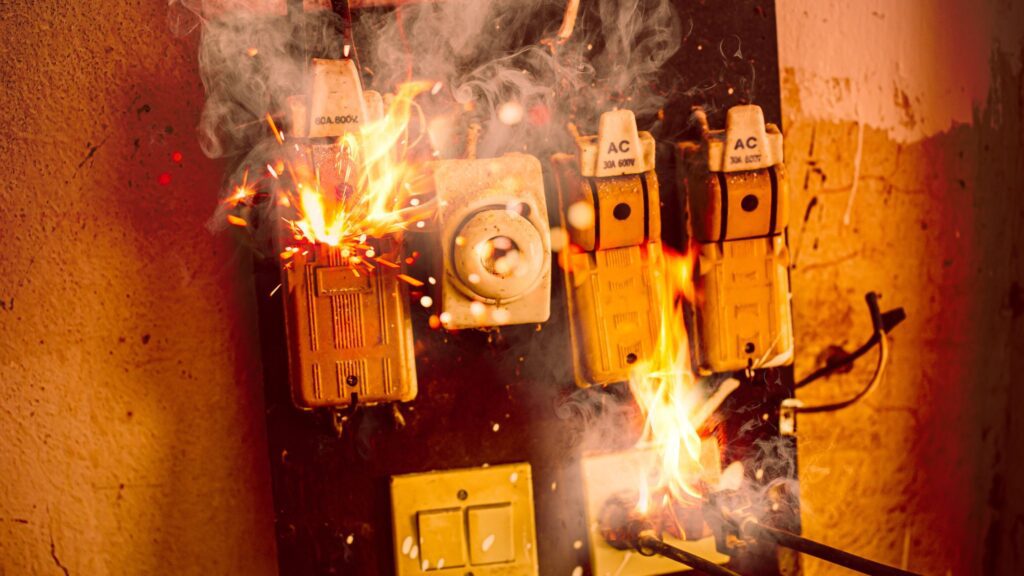
Short Circuit
A short circuit is essentially an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path. It occurs when an accidental low-resistance path forms between two points in a circuit, bypassing the intended load. This can result in a surge of current, overheating, and potentially a fire hazard. Be careful to avoid!
Fuse
A fuse is a safety device designed to protect electrical circuits from excessive current. It contains a metal wire that melts when the current exceeds a certain level, breaking the circuit and preventing damage.
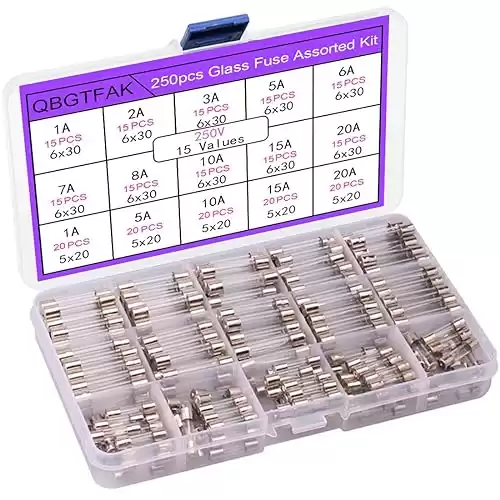
For a reliable assortment of fuses, consider the 250pcs Quick Blow Glass Tube Fuse Assorted Kit 250V 1A, 2A, 3A, 5A, 6A, 7A, 8A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 6x30mm, 250V 1A, 5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 5x20mm (5x20mm and 6x30mm). This kit offers a variety of quick-blow fuses perfect for different applications, ensuring your circuits are well-protected.
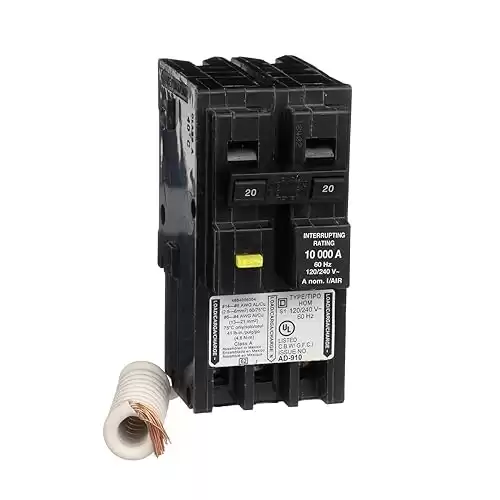
Circuit Breaker
Similar to a fuse, a circuit breaker is a safety device that automatically shuts off the flow of electricity when it detects an overload or short circuit. Unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be reset after tripping.
Similar to a fuse, a circuit breaker is a safety device that automatically shuts off electricity when it detects an overload or short circuit. Unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be reset after tripping. The Square D - HOM220GFIC Homeline Circuit Breaker, 20-Amp, 120/240V, 2-Pole, GFCI, Plug-In Mount provides reliable protection and easy resetting for your electrical systems.
Charge Your Intelligence!
Understanding these vital terms can empower you to tackle your electrical projects safely and effectively. Whether you’re changing a light fixture or troubleshooting a faulty outlet, having a firm grasp of the basics will enhance your confidence and ensure a smoother (and hopefully shock-free) electrical experience. So the next time you’re confronted with jargon from the electrician, you’ll be prepared to surprise them with your new knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Voltage In Electrical Terms?
Voltage, or potential difference, is the force that pushes electricity through a wire. It is measured in Volts (V) and represents the energy behind the flow of electricity.
How Is Electrical Current Defined?
Electrical current is the flow of electricity through a conductor, like a wire. It’s measured in Amps (A) and indicates the rate at which electrical charge flows.
What Does Electrical Resistance Mean?
Electrical resistance is the opposition to the flow of electrical current. High-resistance materials, like rubber, restrict flow, while low-resistance materials, like copper, allow current to flow easily.
What Is The Purpose Of Grounding In An Electrical Circuit?
Grounding provides a safe path for excess electricity to flow into the ground, preventing electrical shocks and fire hazards. It’s a crucial safety feature in electrical systems.
How Do Fuses And Circuit Breakers Protect Electrical Circuits?
Fuses and circuit breakers are safety devices that prevent excessive current flow. Fuses melt to break the circuit when overloaded, while circuit breakers trip and can be reset after an overload or short circuit.