The place you work every day is an office building whose temperature and the quality of its indoor air matter as far as your comfort and productivity are concerned. Have you ever thought about how the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system does to manage your environment? You must have a grasp on the basics of HVAC systems to enable you to make informed choices as a tenant and optimize conditions for your workspace. Our article introduces readers to the main types of equipment used in HVAC systems, the way they work, and how they are maintained.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is HVAC? Defining Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning
Heating
- Heating refers to the method employed for maintaining comfortable indoor temperature through the creation or transfer of heat. Popular heating means include furnaces, heat pumps, and boilers. Furnaces produce warm air which travels through ducts but boilers warm water or steam that circulates throughout buildings. When it comes to heat pumps, they use electricity to push warmth from low-temperature areas into high-temperature ones.
Ventilation
- By definition, ventilation entails bringing clean outdoor air into buildings while removing stale indoor air. Ventilation networks such as ductwork, vents, fans, and filters facilitate the exchange of fresh air with stagnant internal one. Proper ventilation also ensures better IAQ (indoor air quality) by controlling moisture levels.
Air Conditioning
- Inside buildings, air conditioning systems cool and dehumidify the air to create a comfortable atmosphere. These work like fridges by using refrigerant and coil systems to remove heat and moisture from the air. There are two major types of air conditioners: unitary systems for individual rooms and central systems for entire buildings.
Integrating the Systems
- Additionally, modern heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems can be combined into one integrated system that serves residential homes and commercial properties where they are controlled by a thermostat. This has allowed them to regulate temperature as well as humidity throughout all seasons for both domestic and industrial purposes. Besides, advancements in technology have made HVACs more energy efficient, environmentally friendly as well as automatic. Therefore, proper maintenance such as filter cleaning or replacement is important to keep your HVAC functioning safely and consistently.
HVAC System Types: Split, Packaged, Central, Window
Split Systems
- They have two components that make up split HVAC systems— an outdoor unit and an indoor unit. The indoor unit usually located within a utility closet, basement, or attic; circulates cooled or heated air around the structure. The condenser and compressor are found in the outdoor unit. Split systems are very efficient hence enabling higher energy performance although installation costs tend to be higher due to the extra line set needed to connect indoor units with outdoor ones.
Packaged Systems
- Packaged HVAC systems have all components located in a single outdoor unit. The unit circulates cooled or heated air through ductwork that distributes it throughout the building. Packaged systems typically have lower upfront costs and are simpler to install compared to split systems. However, they usually have lower energy efficiency and can produce more noise. They are best suited for small commercial buildings or residential units.
Central HVAC Systems
- Central HVAC systems have components located in both indoor and outdoor units. An air handler circulates cooled or heated air through a network of supply and return air ducts in the building. A condenser and compressor are located in an outdoor unit. Central systems provide even temperature control throughout the building but have high installation and operating costs. They are typically used in large commercial buildings.
Window HVAC Units
- Window units are self-contained systems installed in a window or wall opening. They draw in outside air, cool or heat it, then exhaust it outside. Window units are inexpensive and easy to install but are typically less energy efficient. They are best suited for cooling or heating a single room. For the most efficient use, ensure the unit is properly sized for the space.
HVAC Applications: Residential, Commercial, Industrial
Residential HVAC
Residential HVAC systems are designed to provide temperature and humidity control of houses. The most typical ones are the central forced air systems that move air via ductwork or mini-split systems having an outdoor compressor and one or more indoor air handlers. Residential heating, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) units mainly use natural gas, propane, or electric heating and can also include such additional features as filtration, humidification, and zoning for improved comfort.
Commercial HVAC
On the other hand, commercial HVAC is used in diverse environments like offices, retail spaces, hospitals, and schools among others. These are large-scale appliances with higher capacity to condition larger space volumes. Commercial HVAC consists of ventilation; humidity control; and air cleaning besides the cooling and heating processes. Some devices also have heat recovery ability thus enhancing energy efficiency by reclaiming heat from one area of a building to be used in another area. It is essential to consider factors such as the size of the building being served, use of the building itself, type of construction materials used during its erection as well as climatic conditions specific to that particular region when selecting a suitable HVAC system.
Dive into 'The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners,' your ultimate guide to mastering HVAC systems. From installation to troubleshooting, this updated manual covers it all for both residential and commercial use. Ideal for beginners and experienced technicians seeking comprehensive expertise.
Industrial HVAC
Industrial HVAC systems serve manufacturing facilities on a large scale where they provide heating cooling and ventilation services apart from warehouses. They require much bigger capacities and performance levels than what could be found with areas up to 100000 square feet. Industrial HVAC may incorporate large chillers, cooling towers, air handlers, and ventilation equipment to handle the facility’s high heat loads and air circulation needs. Additional capabilities like humidification, dehumidification, and air purification are common. The HVAC design considers factors such as the operational requirements of equipment, storage conditions for materials, and health and safety standards for employees.
HVAC Maintenance and Repairs
To ensure optimal performance and efficiency, HVAC systems require routine maintenance and occasional repairs. As an HVAC system ages, components can deteriorate or break down, reducing heating and cooling capacity.
Filter Changes
- HVAC filters remove airborne particles like dust, pollen, mold, and pet dander. Clogged or dirty filters reduce airflow and efficiency. It is recommended that HVAC filters be inspected monthly and replaced every 90 days. Failure to change filters regularly can damage the HVAC unit and reduce its lifespan.
Coil Cleaning
- The evaporator and condenser coils in an HVAC system can become coated with debris over time. A professional can spray the coils with a detergent to loosen buildup and then rinse them with a high-pressure hose. Coil cleaning improves heat transfer and increases efficiency. It should be performed every year or two depending on run time and environmental conditions.
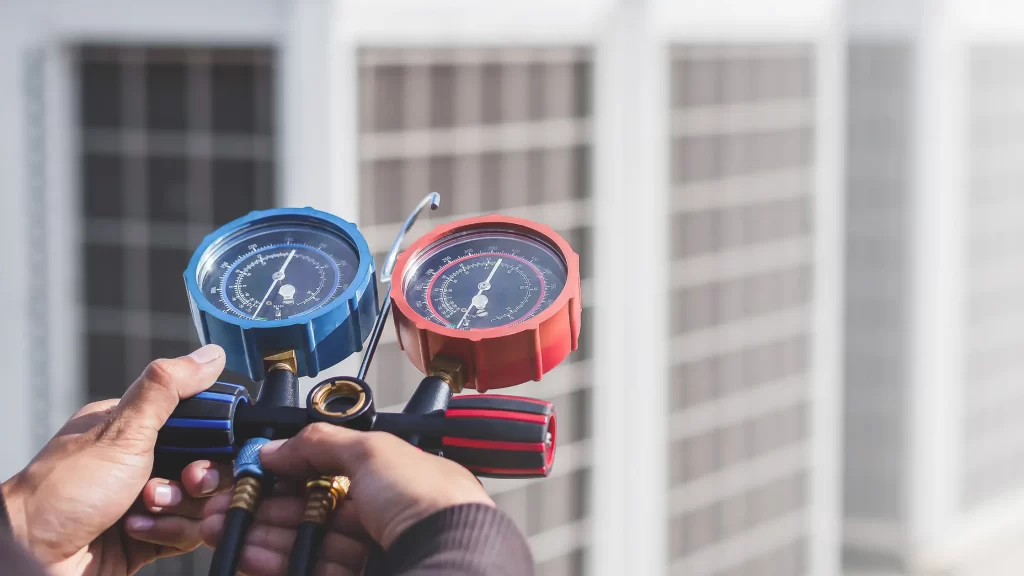
Refrigerant Levels
- The refrigerant absorbs heat from indoor air to cool it down within an HVAC system. When the refrigerant levels are low, the system has more work to do to cool properly. To check the levels of refrigerants and recharge where applicable should be done by an AC technician. The purpose of recharging refrigerant is to ensure maximum cooling capacity and efficiency.
What Is HVAC
As an overview, HVAC systems are very complicated and encompass numerous components that work together to produce warmth, ventilation, cooling, humidity control, and air purification in buildings. With consistent maintenance by accredited technicians, however, these systems can provide comfortable and healthy interiors for many years. If you are a building owner or facilities manager though it is important to know some basics on how HVAC works and the different types of systems available so that you can make informed decisions when installing new ones or upgrading the existing ones.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does HVAC Stand for?
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning. It refers to the systems used to control indoor temperature, air quality, and humidity.
How Does HVAC Work?
HVAC systems regulate indoor conditions by heating or cooling air, circulating it through a building via ductwork, and removing stale air while bringing in fresh outdoor air through ventilation.
What Are the Main Components of an HVAC System?
The main components include heating units (like furnaces or heat pumps), ventilation systems (ductwork, vents, and fans), air conditioning units (using refrigerant and coil systems), and thermostats for control.
What Are the Different Types of HVAC Systems?
HVAC systems can be split into various types such as split systems, packaged systems, central HVAC systems, and window units, each suited for different building sizes and layouts.
Why Is HVAC Maintenance Important?
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance, energy efficiency, and longevity of HVAC systems. Tasks like filter changes, coil cleaning, and checking refrigerant levels are crucial for maintaining indoor comfort and air quality.
How Much Does HVAC Make?
The income in HVAC varies based on factors like location, experience, and specialization. On average, HVAC technicians earn around $50,000 to $60,000 per year, but this can increase with advanced skills and certifications.