In the ever-evolving landscape of architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC), two essential technologies have emerged as game-changers: Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Building Information Modeling (BIM). These tools revolutionized the way professionals design, plan, and execute projects, streamlining processes and enhancing collaboration. We’ll delve into the details of these impressive technologies, laying out what they are, what they do, how they work, and the key differences between them.
Table of Contents
Toggle
What is CAD?
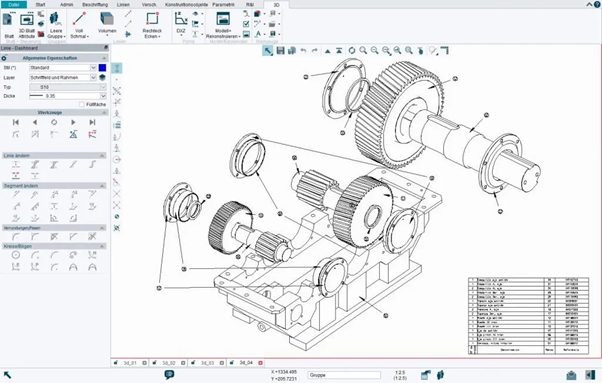
Computer-Aided Design is a computer software that enables architects, engineers, and designers to create, modify, analyze, and optimize digital representations of physical objects. These can range from simple 2D drawings to intricate 3D models of buildings, products, or mechanical components. CAD software provides a virtual canvas where professionals can draft and visualize ideas before they are built in reality.
What does CAD do?
- Design and Drafting: CAD tools allow users to create accurate, scaled drawings and models of objects, facilitating the design process and enabling rapid iterations.
- Precision and Accuracy: CAD software ensures precise measurements, angles, and proportions, eliminating human errors that could impact the final product’s quality.
- Visualization: CAD models provide a visual representation of concepts, aiding in better communication with clients, stakeholders, and project teams.
- Documentation: CAD generates detailed documentation, such as plans, elevations, sections, and construction details, essential for construction and regulatory compliance.
What is BIM?
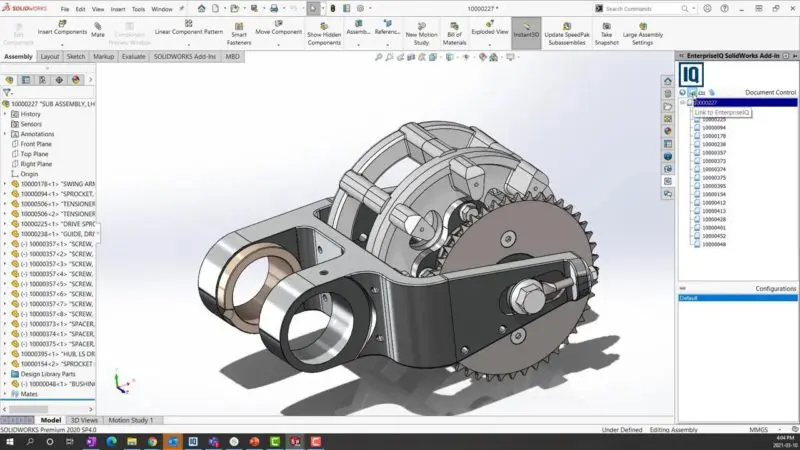
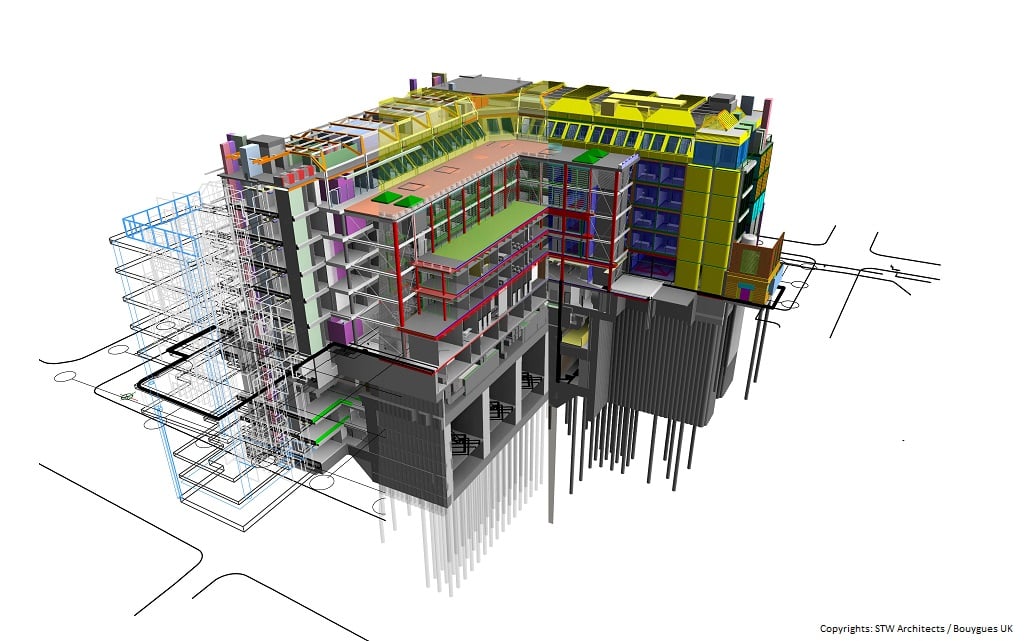
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a collaborative process that utilizes digital models to represent the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure. BIM goes beyond traditional CAD by integrating various aspects of a project, including geometry, spatial relationships, data, and metadata.
What does BIM do?
- Data Integration: BIM combines graphical and non-graphical information, such as costs, materials, schedules, and performance data, to provide a comprehensive understanding of a project.
- Lifecycle Management: BIM supports the entire lifecycle of a structure, from initial design through construction, operation, and maintenance, making it a valuable tool for facility management.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: BIM encourages collaboration among different disciplines by enabling real-time sharing of information and reducing conflicts and errors.
- Simulation and Analysis: BIM allows for simulations and analyses like energy performance, clash detection (identifying conflicts between different systems), and structural analysis, aiding decision-making.
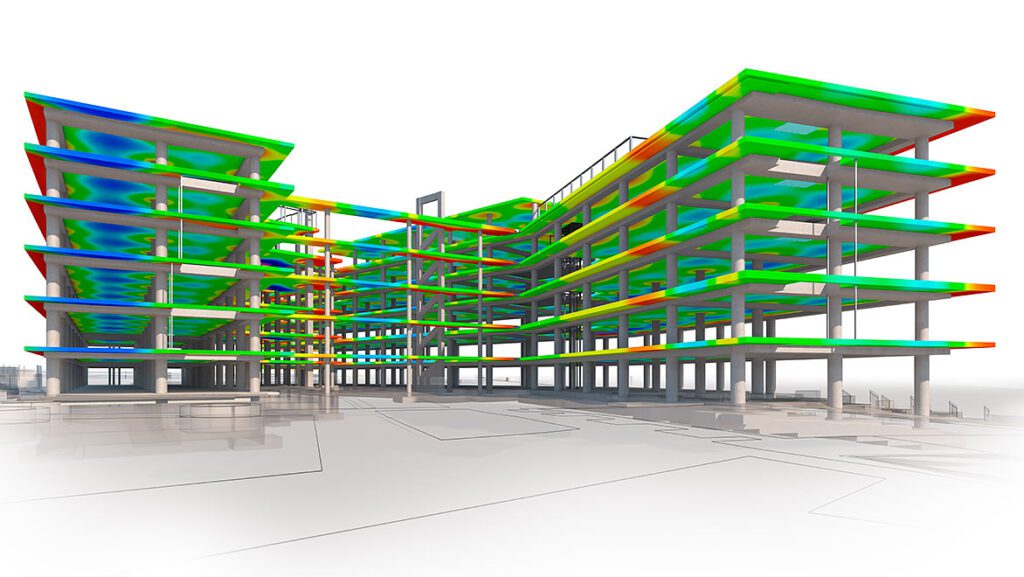

The Difference between CAD and BIM
Imagine you’re building a puzzle. CAD helps you draw pieces of the puzzle, making sure each one fits perfectly and looks great on its own. It’s very good at creating accurate pictures of individual pieces.
On the other hand, BIM is like putting the puzzle together in a smart way. It not only includes the pictures of the pieces (like CAD), but it also knows how each piece connects to the others. It has information about the materials, sizes, costs, and even how the puzzle changes over time. BIM helps people work together better because everyone can see how their pieces fit with everyone else’s.
More specifically, here are some clear distinctions between the two:
- Level of Detail: CAD focuses mostly on geometry, while BIM incorporates both geometry and data, providing a more complete view of the project.
- Collaboration: BIM emphasizes collaboration across multiple disciplines and phases of a project, fostering better communication and reducing conflicts.
- Lifecycle Integration: BIM covers the entire lifecycle of a project, from design to operation, making it a powerful tool for facilities management.
- Information Depth: BIM provides deeper information about components, materials, costs, and performance, aiding decision-making.
BMI vs CAD
In the AEC (architecture, engineer, and construction) industry, both of these softwares have significantly transformed the way projects are designed, planned, and executed. CAD focuses on precise drafting and design, while BIM encompasses a broader, more collaborative approach that integrates data, disciplines, and project phases. Understanding these technologies empowers professionals to harness their capabilities effectively, resulting in more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable projects. As the industry continues to evolve, CAD and BIM will remain at the forefront, driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in architecture and construction.




2 thoughts on “BIM vs CAD: Understanding the Difference ”
Excellent blog you have got here.. It’s difficult to find high quality writing like yours these days. I truly appreciate people like you! Take care!!
We greatly appreciate this comment, Alberto! Thank you for reading our content. Have an awesome week.